Who knew there’d be a day when our health diagnosis and treatment will be just a few clicks away.
Telemedicine isn’t an unknown term to the healthcare sector around the world. In fact, it has been around for the past few decades. Telemedicine started to gain pace in 2005. It wasn’t until 2015 that it exploded into a billion-dollar industry around the world.
Telemedicine is rapidly becoming the new normal in healthcare. According to a survey conducted by the American Hospital Association (AHA), the use of telehealth in hospitals increased from 35% in 2010 to 76% in 2017.
In Pakistan, telemedicine is now one of the top booming platforms with a very high success ratio. Many new telehealth startups have shared their success stories and are keen to further invest in e-healthcare in Pakistan. For instance, emeds.pk is a licensed online pharmacy that provides free online consultation with certified pharmacists for various health problems. It is the only online retail pharmacy with ISO 9001-2015 certification in Pakistan. It also ranked 2nd in healthcare in the e-Commerce Awards 2020 because of its strict rules and outstanding customer service.
What is Telemedicine?
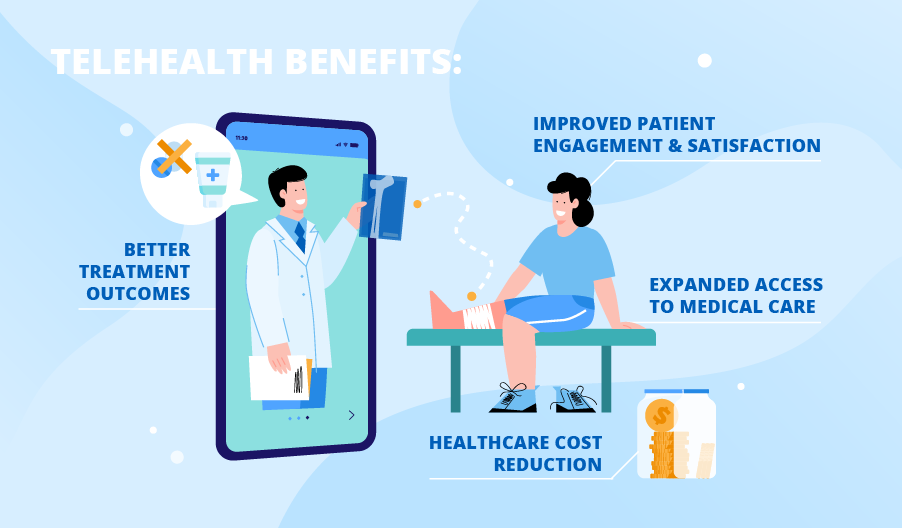

Telemedicine provides remote healthcare services through real-time, direct communication between the patient and the doctor by utilising technological devices.
Telemedicine is beneficial in cases of non-emergency consultations and diagnosis. Patients can be given medical advice through phone or other electronic means. In this way, patients can receive immediate medical attention while also providing relief to on-duty healthcare workers.
The purpose of telemedicine isn’t replacing in-person consultation when it’s necessary; rather, it complements the system.
How COVID-19 Affected Telemedicine Around the World


Many developed countries such as China, UK, USA, Singapore, Switzerland, Ireland, Finland, Greece, Austria, Belgium, Poland, etc., were already using telehealth and telemedicine within their healthcare sector. It wasn’t until the onset of COVID-19, the field of telemedicine blew up into a billion-dollar industry all across the globe. Healthcare institutions around the world developed ways to provide both in-patient and out-patient services via telemedicine.
One of the main reasons telemedicine is such a big hit is that it enables patients and doctors to connect remotely. Healthcare professionals can provide medical assistance to the patients while practising social distancing. It is also a faster and more efficient way than the process of waiting for your appointment and over-crowding the hospitals, particularly during the global pandemic.
Telemedicine can significantly benefit patients who don’t need any immediate medical aid but require a dosage adjustment, lifestyle changes, dietary plans, prescription, or even peer support. Such healthcare services can be arranged conveniently using a phone or any other electronic means at any given time.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, telemedicine played a crucial role in protecting personal protective equipment (PPE) during a universal shortage. It protected the front-liners from being infected by minimising in-person exposure and enabled monitoring patients’ chronic conditions without increasing the risk of getting infected by attending medical setups.
Successful Telemedicine Framework From Various Regions

Singapore: Singapore is Asia’s unbeatable beast when it comes to telemedicine and healthcare system efficiency. In 2018, the Singapore Ministry of Health initiated steps to support innovation and promote relationships between government and telehealth partners.
China: In September 2018, the National Health Commission and the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine published new e-healthcare rules to improve telehealth potential and develop the e-healthcare industry.
Kazakhstan: In 2005, Kazakhstan launched the first massive project known as “Development of Telemedicine in Rural Healthcare” within the state policy framework. In 2018, a five-year state program, “Digital Kazakhstan”, was launched in which five key areas, including medicine, are intended for digital transformation.
UK: Telecommunication companies such as Virgin Media, Sky and BT in the United Kingdom have decided to facilitate the National Health Services (NHS) in rolling out telehealth for healthcare workers. Medical services, including primary care, clinical examinations, chronic illness surveys, and counselling, are quickly moved to telehealth delivery. Before COVID-19, the UK government had already confirmed a state-financed “Long Term Plan” to decrease the number of out-patient demonstrations.
USA: During the COVID-19 pandemic, Medicare in the United States will be now in charge of covering qualified telehealth meetings, while individual states are also being encouraged to roll out Medicaid cover for such medical assistance. Likewise, the Federal Communications Commission launched a $200 million Coronavirus Telehealth Program to modify and develop its healthcare industry.
Telemedicine Framework in Pakistan


Pakistan has an auspicious future in the telemedicine and telehealth industry.
Since the outbreak of the coronavirus pandemic, telemedicine has become one of the top thriving platforms in Pakistan. One of the primary reasons behind its popularity is that people can get timely access to medical services.
The Healthcare sector in Pakistan is sprained and fractured. As a result, many lives are lost daily due to the lack of or delay in medical aid, particularly in rural parts of the country. Telemedicine is proving to be a great asset regarding this issue.
Likewise, telemedicine and e-healthcare have opened doors of employment for the many medical professionals in Pakistan since 70% of all medical students are women, and most of them usually leave midway through their profession.
In this COVID-19 pandemic, there is a constant shortage of eligible medical practitioners as the number of cases is still on the rise. Hospitals are facing a crisis due to a lack of medical staff and resources. During these challenging times, telemedicine is playing a significant role in aiding the people in need.
Challenges to Overcome for A Better Tomorrow

Pakistan is an overpopulated country where the healthcare sector faces unique challenges, including socioeconomic, geographic, and political challenges. As much as this pandemic is nothing but a global catastrophe, it did bring an unexpected opportunity for Pakistan to recognise many shortages in healthcare through telemedicine. Therefore, it’s time for Pakistan to step up its game by making policies and strategies for telemedicine’s productive use.
By identifying the problems and looking for the best solution, telemedicine may prove to be a significant asset for improving healthcare in Pakistan. Over a couple of years, it has been motivating and encouraging to see more doctors adopting telemedicine and the interest of nonprofit organisations and academic institutions.
Telemedicine is a platform that requires a team effort to succeed. It’s necessary to maintain a healthy doctor-patient relationship for an effective healthcare system. It’s time for us to face the challenges and go the extra mile to strive towards a common goal for a better tomorrow.




