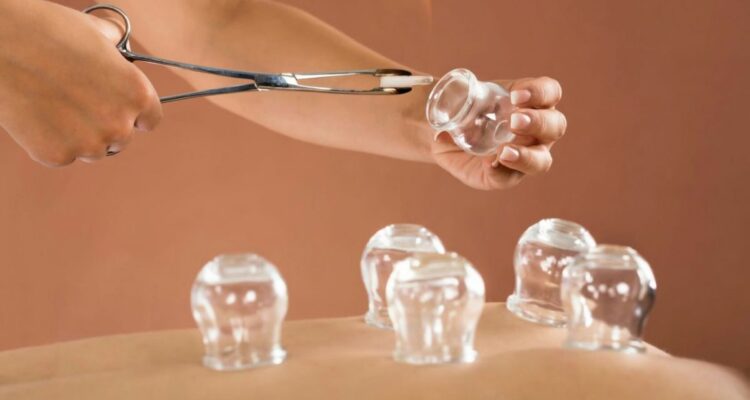
In this modern era, Hijama therapy is also called Cupping therapy. Hijama means vacuum or suction. Suction cup therapy is an ancient method that has been used for centuries for various painful conditions. It is performed by applying cups to selected points of the skin, most commonly on the back, in order to create areas of subatmospheric pressure.
It was classified as a type of dry or wet therapy. It is relatively safe, with some reported side effects, which include scarring and skin infection. It has been traditionally used for the treatment of painful conditions but has also been used to treat chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorder, skin disease and metabolism disease Benefit of having Hijama is that reduces pain, particularly in musculoskeletal conditions, such as low back pain and neck pain.
It is based on the assumption that “pain inhibits pain,” or one type of pain masks another when two painful stimuli are applied simultaneously. According to the theory, scratching done during cupping therapy causes a nociceptive stimulus which eventually leads to the relief of the primary pain.
If you are in Islamabad and looking forward to having Hijama you should visit the authentic center, I would suggest HIjama Center Islamabad
Type of Hijama:
- Dry Cupping
- Wet Cupping
- Moving Cupping
Dry Cupping:
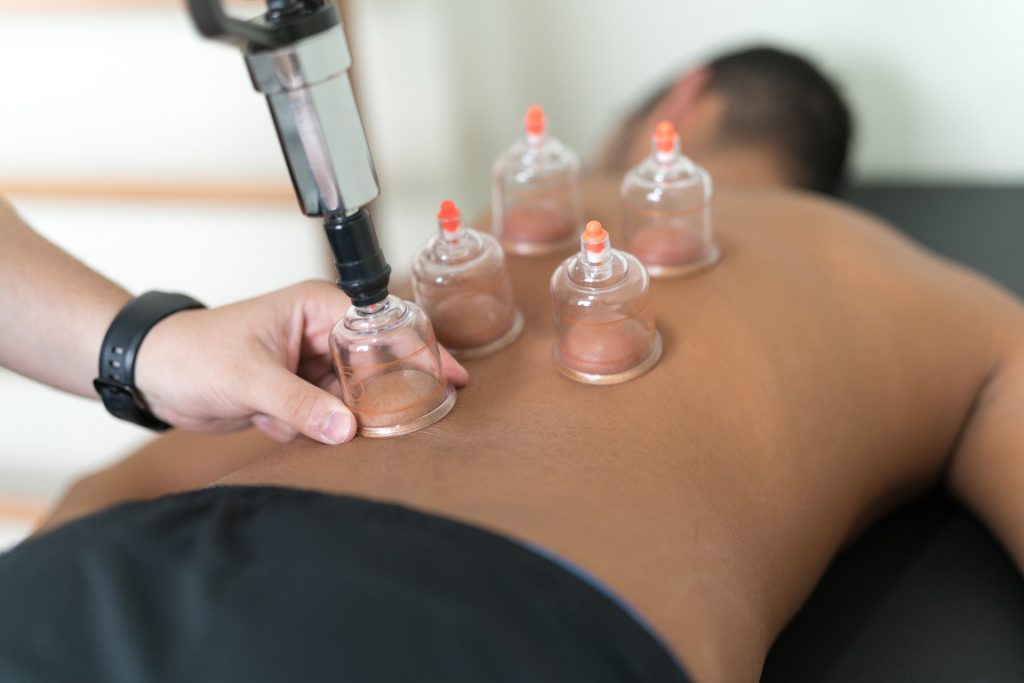

The dry cupping is also known as the static suction cup or the suction cup. In dry Cupping, negative pressure is generated inside the cups by different forms of suction, such as fire, hand pump, or electric suction. Cups are usually kept on the skin for up to fifteen minutes. When a hand pump is used, the pressure inside the cup is controlled by the number of suctions. As the number increases, the negative pressure inside the cup will increase. Likewise, when the fire is used, the exposure to fire will increase the negative pressure inside the cup. This negative pressure leads to protrusion of the skin
Wet Cupping:
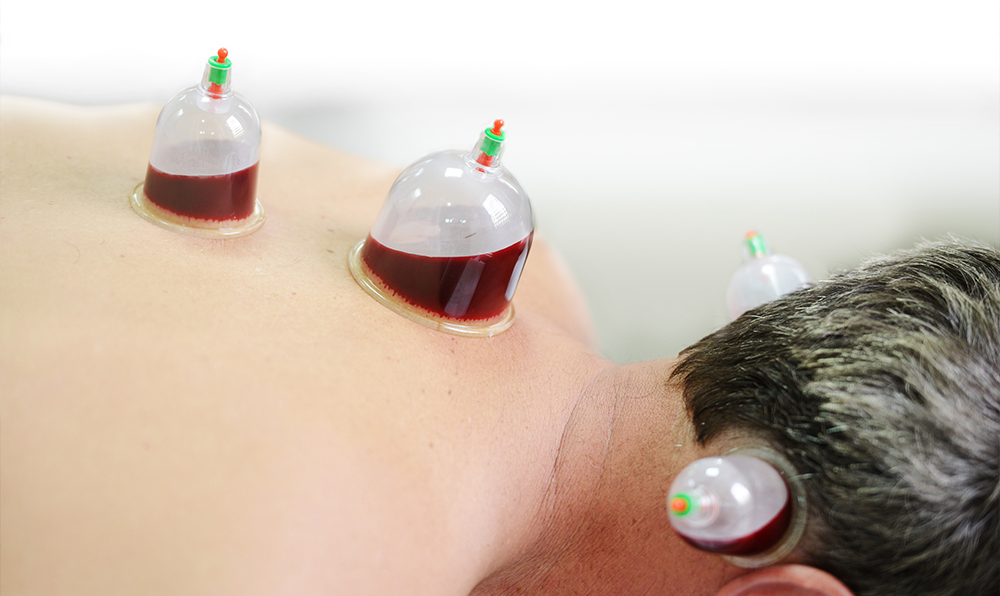

Wet cupping creates a mild suction by leaving a cup in place for about 3 minutes.
The therapist then removes the cup and uses a small scalp to illuminate tiny cuts on your skin. After the first suction, time to do a second suction to draw out a small quantity of blood.
You will get 3-5 cups in the first session. Or you can try one to see how it goes.
Afterward, you may get an antibiotic ointment and bandage to prevent infection. Your skin should look normal again within 10 days.
The wet suction cup creates a smooth suction, leaving a cup in place for about three minutes.
The therapist then removes the cup and uses a small scalp to illuminate., tiny cuts on your skin. Then they do a second suction to draw a small amount of blood.
You can get 3-5 cups in your first session. Or you can just try one to see how it works. It is not common to get more than 5 to 7 cups.
After that, you will have an antibiotic ointment and to prevent infection. Your skin will get normal in 10-15 days.
Moving Cupping:
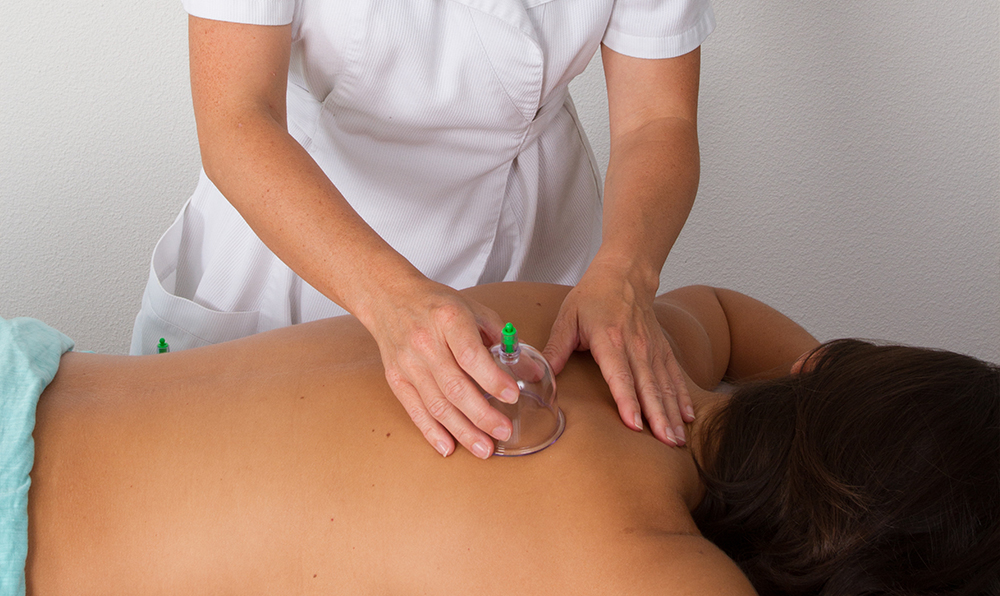

The Moving cupping is also known as Massage cupping, dynamic cup, and sliding cup. It is done by applying oil to the skin and moving the cups over the treated area by means of weak suction. Different types of oils are used, such as olive oil, peppermint oil, and lavender oil. This type of suction cup can be used by young and old
Back pain:
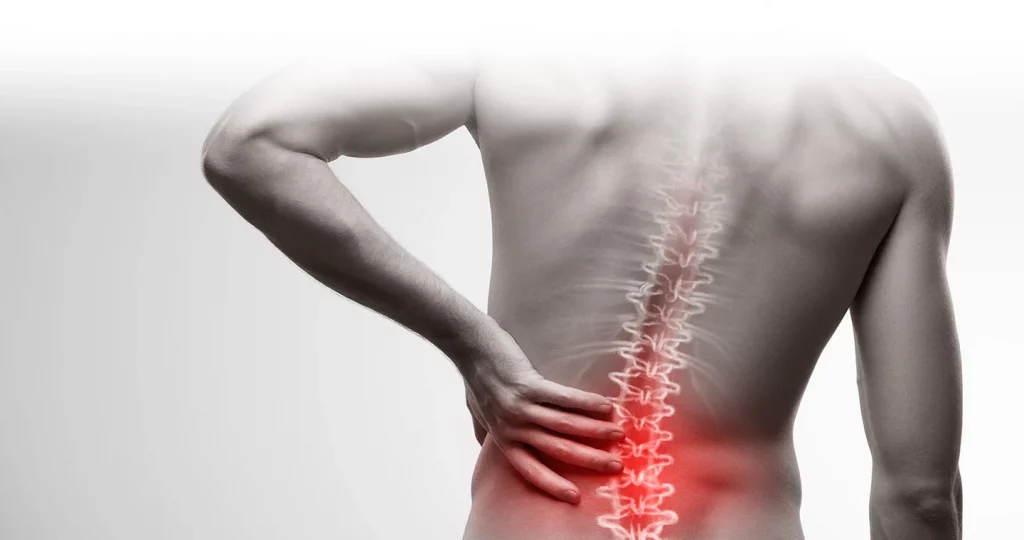

Low back pain is a common clinical problem. Current management options include bed rest during the acute phase, analgesia, physical therapy, traction, alternative treatments, and health education on preventing the future. Suction cup therapy has long been used for acute and chronic low back pain. Studies have shown a significant reduction in pain intensity scores and improvement in the functional results with excavation tools compared to other treatment modalities. Different types of suction cups were used in these tests (3 dry suction cups, 2 wet suction cups, 1 mobile suction cup). The pain was measured by different tools. The meta-analysis concluded that excavation therapy was more effective compared to other modalities. Most studies that included patients with low back pain investigated the short-term effects of the excavation and were conducted for 2 to 12 weeks only.
Neck pain:
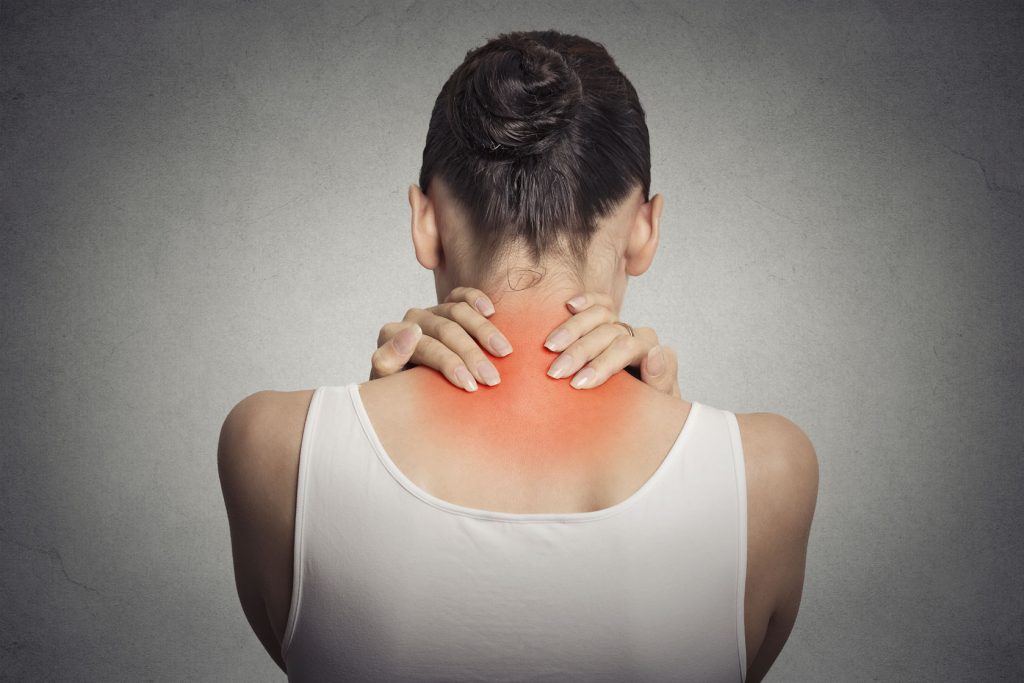

The prevalence of neck pain throughout life varies from 14.2% to 71% and is more dominant in the age groups with high activity, especially in the age group 35 to 49 years. It has been found to be associated with higher medical costs and adverse effects on personal productivity. The therapies commonly used for neck pain include the use of pain relievers and physical therapy.
In addition, surgery can help in some specific situations. However, these options are not always effective and are sometimes associated with serious side effects. Therefore, people have always looked for other alternative options that include traditional medicine.
Suction cup therapy is one of the methods commonly used by people to relieve neck pain, especially for non-specific types. Studies carried out in patients with this condition. In conclusion, the best way to treat neck therapy is by cupping or having hijama.
Complication Of Hijama:
Cupping therapy is generally considered to be a safe treatment, with minor side effects and complications. However, the safety of suction cup therapy is poorly reported.
Most of the studies carried out mainly addressed its effectiveness, but only a few studies reported its complications. The commonly recognized side effects are erythema, edema, and ecchymosis, which are caused directly by the excavation.
Skin burns have also been reported. They can occur for the following reasons: excessive use of alcohol, prolonged exposure to suction cup therapy, sensitive skin, especially in the elderly, and use of fire.
Conclusion:
Cupping therapy is an ancient complementary medicine practice that has been used for thousands of years for a variety of common medical problems. Current evidence suggests that suction cup therapy may be effective in treating common chronic pain conditions for a short time. However, most of the available studies have important limitations, such as small sample sizes and different tools for evaluating results, duration of treatment, and treatment regimens.




